What Is Bitcoin?
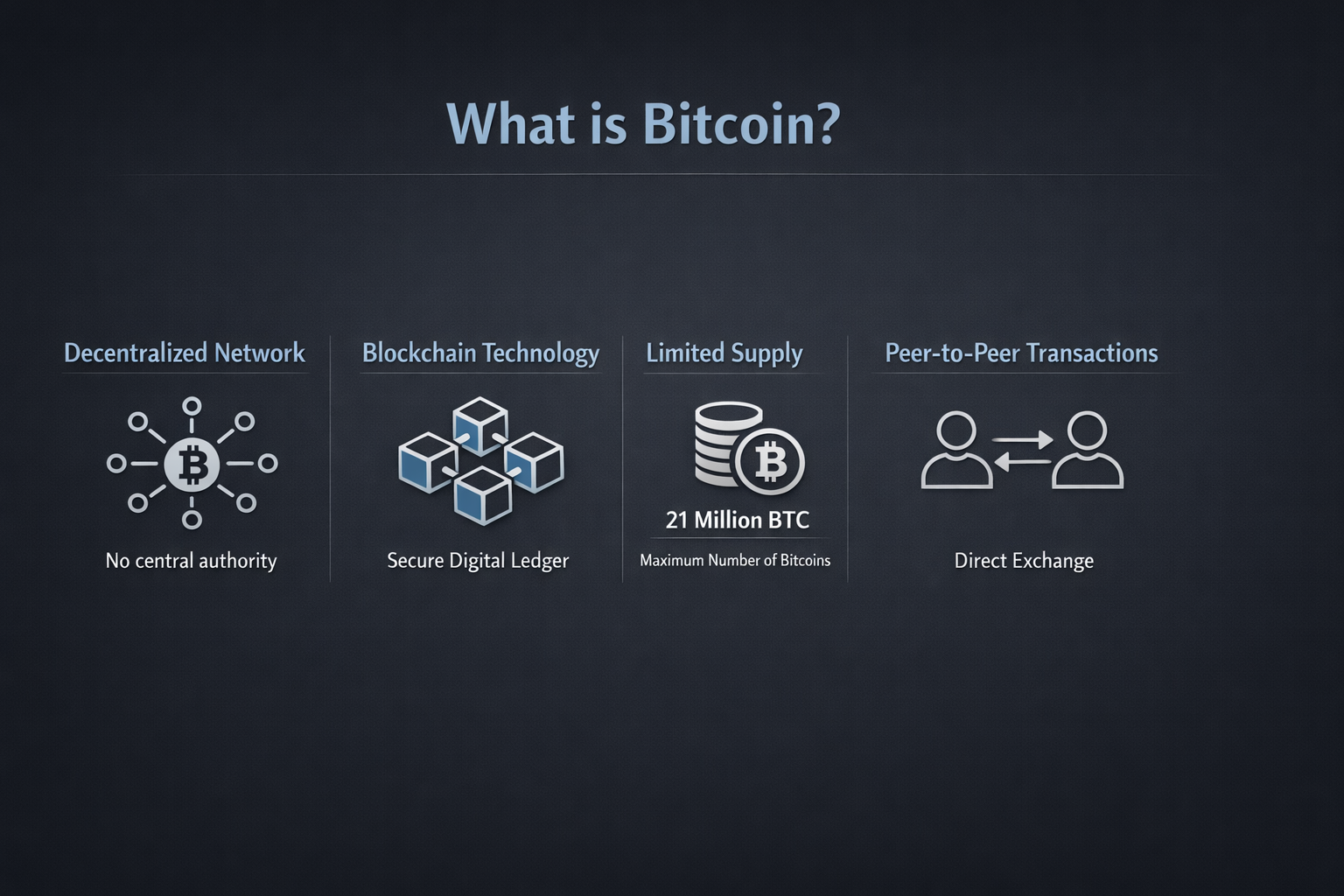
Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency that allows people to send and receive money over the internet without banks or central authorities. It operates on a public blockchain network where transactions are verified by distributed computers instead of a single institution.
Launched in 2009, Bitcoin introduced a new financial model based on transparency, scarcity, and mathematical rules rather than trust in intermediaries.
Bitcoin Explained in 4 Layers
1.Technology Layer
Bitcoin runs on blockchain technology and cryptographic verification.
2.Monetary Layer
Supply is capped at 21 million coins, creating digital scarcity.
3.Network Layer
Thousands of independent nodes validate transactions globally.
4.Market Layer
Price fluctuates based on supply, demand, sentiment, and liquidity.
1. Why Was Bitcoin Created?
Bitcoin was created in response to weaknesses in traditional financial systems. During financial crises, banks and institutions can fail, freeze withdrawals, or require government intervention. Bitcoin was designed to function independently of these systems.
Its goal was to create a form of money that follows transparent rules, cannot be easily manipulated, and does not rely on trust in a single authority.
2. How Bitcoin Works
Bitcoin operates on a public network known as a blockchain.When a transaction is confirmed, it becomes part of a block. Once added, blocks cannot be easily altered, making the system transparent and resistant to fraud.
3. What Is Bitcoin Mining?
Bitcoin transactions are verified through a process called mining. Miners use computing power to validate transactions and secure the network.
In return for their work, miners receive newly issued bitcoins. This process ensures that no single participant can control transaction history or create fake transactions.
How Bitcoin Mining Works (Simplified)
4. Limited Supply and Scarcity
Bitcoin has a fixed supply limit of 21 million coins. This limit is enforced by the software and cannot be changed without network-wide agreement.
Unlike traditional currencies that can be printed in unlimited quantities, Bitcoin’s supply decreases over time, making it a scarce digital asset.
5. What Bitcoin Is Not
Bitcoin is often misunderstood. It is not a company, stock, or government-backed currency. It does not guarantee profits and does not eliminate financial risk.
Bitcoin should be viewed as a technology and an alternative monetary system, not as a promise of returns.
6. Why Do People Use Bitcoin?
People use Bitcoin for different reasons. Some use it for global value transfers, others for financial independence, and some for learning about decentralized systems.
Its open and permissionless nature allows anyone with internet access to participate.
Bitcoin vs Traditional Money
Bitcoin
- Fixed supply (21 million)
- Decentralized network
- Transparent public ledger
- Borderless transactions
- Mathematical monetary policy
Traditional Money
- Unlimited supply potential
- Controlled by central banks
- Opaque monetary policy
- Bank-dependent transfers
- Policy-driven inflation
7. Volatility and Risk
Bitcoin prices can fluctuate significantly in short periods. Price movements are influenced by market sentiment, liquidity, regulation, and global events.
Because of this volatility, Bitcoin involves risk and should be approached carefully, especially by beginners.
8. How to Buy Bitcoin Safely
To buy Bitcoin, users typically create an account on a regulated cryptocurrency exchange, complete identity verification, and fund their account using bank transfer or other payment methods.
Beginners should start small, enable two-factor authentication, and store assets securely. For a detailed safety guide, read our beginner safety guide.
Bitcoin Timeline
Key Takeaways
- Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency
- It operates without banks or central authorities
- Transactions are recorded on a public blockchain
- Supply is limited to 21 million coins
- Bitcoin involves both innovation and risk
Disclaimer: This content is for educational purposes only and does not constitute financial advice.
Related guides
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Bitcoin legal?
Bitcoin is legal in many countries, but regulations vary. Always check local laws before buying or trading.
Who controls Bitcoin?
No single entity controls Bitcoin. It is maintained by a decentralized network of participants worldwide.
Why is Bitcoin volatile?
Bitcoin prices fluctuate due to supply-demand dynamics, investor sentiment, regulation news, and market liquidity.
Can Bitcoin be hacked?
The Bitcoin network itself has never been hacked, but exchanges and wallets can be vulnerable if not secured properly.
Recommended Resources
If you are exploring cryptocurrency platforms, choosing a regulated and well-known exchange is important. Always research independently and understand the risks before using any service.
CoinDCX is one of the popular cryptocurrency exchanges in India, offering access to multiple digital assets with INR support.
Learn more about CoinDCXTo see how real-world events impact crypto markets, explore our crypto news explanations.
©BlockSensus. Information only. Not financial advice.